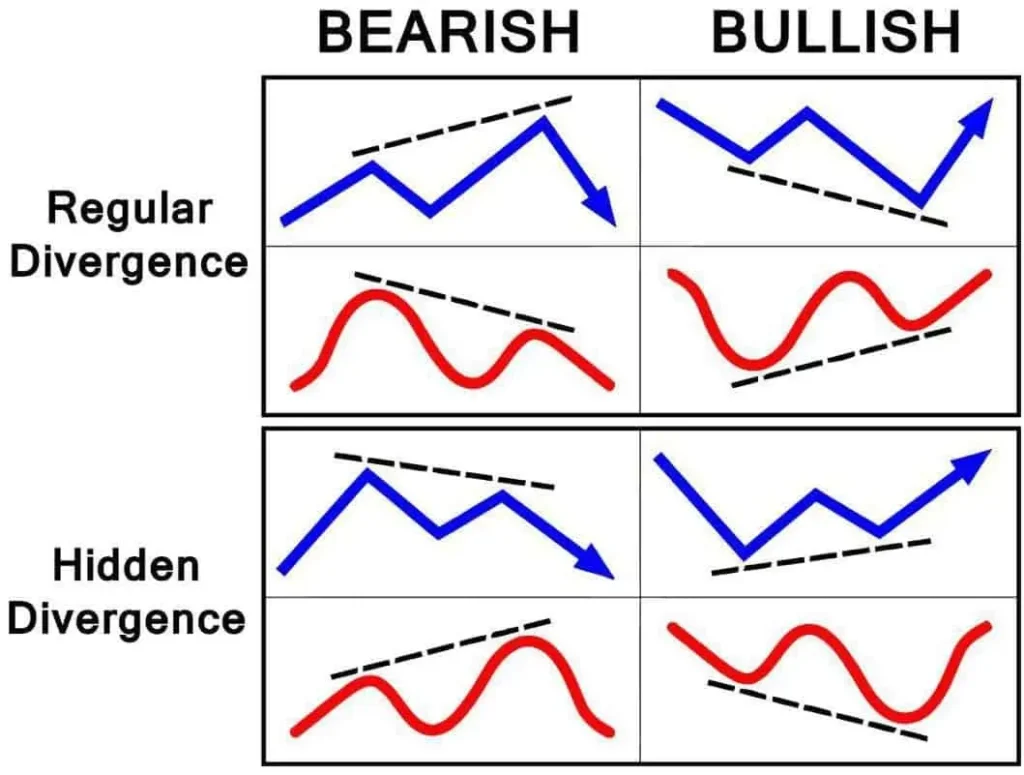
When people think about successful trading, they often focus on technical indicators, chart patterns, and strategies. While these are important, there is one factor that separates consistently profitable traders from struggling ones: trading psychology.
Trading psychology refers to the emotions, mindset, and mental discipline that influence trading decisions. Even the best strategy can fail if a trader cannot control fear, greed, impatience, or overconfidence. In this blog, we’ll explore what trading psychology is, why it matters, common psychological mistakes traders make, and how to build a winning trading mindset.
What Is Trading Psychology?
Trading psychology is the emotional and mental framework that shapes how traders behave in the markets. It includes:
- Emotional control
- Discipline and patience
- Risk tolerance
- Confidence and self-awareness
- Ability to handle wins and losses
Markets are uncertain by nature. Prices move unpredictably, and losses are inevitable. How a trader reacts to this uncertainty defines long-term success far more than any indicator or system.


Why Trading Psychology Is Crucial for Traders
Many traders fail not because their strategy is bad, but because they don’t follow it consistently. Psychology plays a crucial role in:
1. Decision-Making Under Pressure
During fast market movements, emotions can override logic. Fear may cause early exits, while greed can push traders to overtrade or hold positions too long.
2. Risk Management
Proper risk management requires discipline. Emotional traders often increase position sizes after losses or risk too much after a winning streak.
3. Consistency
Consistency comes from executing the same process repeatedly. Psychological instability leads to impulsive decisions and strategy hopping.

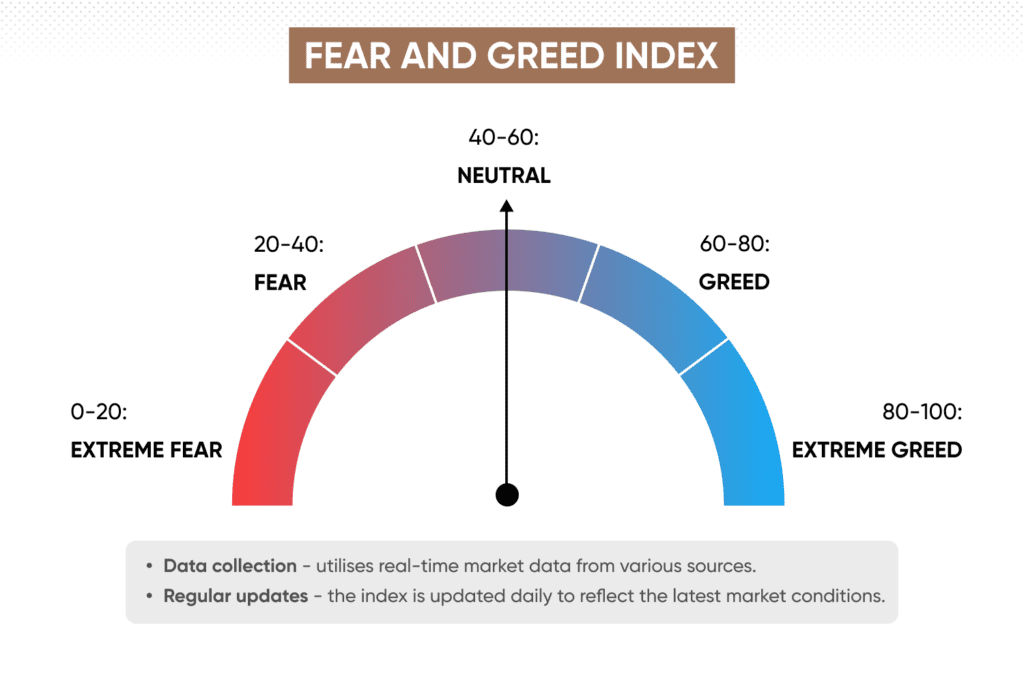

Common Psychological Challenges in Trading
Understanding common emotional traps is the first step toward mastering trading psychology.
Fear
Fear appears in many forms:
- Fear of losing money
- Fear of missing out (FOMO)
- Fear of being wrong
Fear often causes traders to exit winning trades too early or avoid good setups altogether.
Greed
Greed pushes traders to:
- Overtrade
- Ignore stop losses
- Chase unrealistic profits
Greed often leads to blown accounts, especially during winning streaks.
Overconfidence
After a series of wins, traders may believe they’ve “figured out the market.” This often results in excessive risk-taking and ignoring rules.
Revenge Trading
Trying to recover losses quickly leads to emotional trades with poor logic. Revenge trading is one of the fastest ways to damage both capital and confidence.


The Role of Discipline in Trading Psychology
Discipline is the backbone of trading success. It means:
- Following your trading plan
- Respecting stop losses
- Accepting losses as part of the game
- Avoiding impulsive trades
A disciplined trader understands that one trade does not matter, but the outcome of hundreds of trades does.
How to Develop a Strong Trading Mindset
Improving trading psychology is a skill that can be trained. Here are proven ways to build a strong mental edge.
1. Create a Clear Trading Plan
A solid trading plan removes emotional decision-making. It should define:
- Entry rules
- Exit rules
- Risk per trade
- Trading timeframes
When rules are clear, emotions have less control.
2. Practice Proper Risk Management
Risk only a small percentage of your capital per trade (typically 1–2%). This reduces emotional pressure and allows you to think clearly.
3. Keep a Trading Journal
A trading journal helps identify emotional patterns. Record:
- Entry and exit reasons
- Emotional state before and after trades
- Mistakes and lessons learned
Over time, journaling improves self-awareness and discipline.
4. Accept Losses Gracefully
Losses are a normal part of trading. Successful traders focus on process over outcomes. One losing trade does not define your ability.
5. Control Expectations
Unrealistic expectations create frustration and emotional stress. Trading is not a get-rich-quick scheme—it’s a long-term skill.
Trading Psychology and Emotional Control
Emotional control doesn’t mean eliminating emotions—it means not acting on them. Techniques to improve emotional control include:
- Taking breaks after losses
- Avoiding overtrading
- Using meditation or breathing exercises
- Limiting screen time
A calm mind leads to better execution and fewer mistakes.
The Connection Between Mindset and Performance
Your mindset directly affects performance. Traders with a growth mindset:
- Learn from mistakes
- Stay patient during drawdowns
- Focus on continuous improvement
On the other hand, emotional traders often blame the market, indicators, or brokers instead of improving themselves.
Final Thoughts: Master Your Mind, Master the Market
Trading psychology is not optional—it’s essential. Technical analysis and strategies may get you into trades, but psychology determines whether you stay profitable.
If you want long-term success:
- Control your emotions
- Respect risk management
- Stay disciplined
- Focus on consistency, not perfection
Remember, the biggest opponent in trading is not the market—it’s your own mind.